Imaging
MRI is the exam to document the progress of liver and kidney cysts. Certain specialized PKD centers can calculate the blood flow to the kidneys to determine renal perfusion (kidney blood flow) with MRI. According to the PKD CRISP study increased kidney blood flow is the first sign that a treatment is working. The MRI study might be preferable to CT because it uses radio waves with no radiation exposure. Radiation is cumulative over a lifetime. MRI is costly and requires that the individual remain in an enclosed space for a short period of time. There is open MRI but better images are obtained from a closed MRI. CT examination is also useful for following cystic organs though there is added radiation exposure.
MRI
MRI Magnetic resonance imaging is a way of obtaining very detailed images of the body without x-rays, without radiation. Instead, it uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves, a rapidly changing magnetic field, and a computer to demonstrate whether or not there is an injury or some disease process present. MRI is a pulled back view of our organs. It can give organ size and depending on how fine the image slices are, MRI can give a detailed view of the number of cysts present. A patient is placed within the MRI scanner: typically a large, tunnel or doughnut-shaped magnet that is open at both ends. The magnetic field aligns atomic particles called protons that are present in most of the body's tissues. Radio waves then cause these particles to produce signals that are picked up by a receiver within the scanner. There is a newer heart pacemaker that allows MRI images to be taken even with a pacemaker in place.
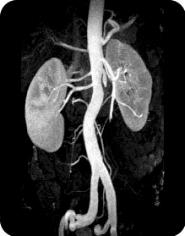
MRA Gadolinium
The FDA is evaluating important safety information about gadolinium- containing contrast agents and a disease known as Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis or Nephrogenic Fibrosing Dermopathy (NSF/NFD) that occurs in patients with moderate to severe kidney failure. New reports have identified a possible link between NSF/NFD and exposure to gadolinium containing contrast agents used at high doses for a procedure called Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA). An MRA test uses magnetic resonance imaging to take pictures of blood vessels. During an MRA test, a drug known as a gadolinium-contrast agent is injected into a vein so blood vessels can be distinguished from other nearby tissues.Nephrogenic Fibrosing Dermopathy NFD/NSF is a skin disease. It does not cause a decrease in kidney functioning. Nephrogenic means the origin is within the kidneys (moderately or severely diminished functioning). The process origin is within the kidneys however nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy is not a cause for diminished kidney functioning. It is similar to a rheumatoid disease of the skin that becomes systemic.
Rarely is gadolinium dye given with concurrent kidney disease. Following giving gadolinium, some doctors may insist upon giving the person copious amounts of fluid and even large doses of vitamin C.
MRA Aneurysm
For purposes of finding a cerebral aneurysm, MRA has totally replaced the need for a catheter threaded x-ray angiography. MR Angiography is a noninvasive method to evaluate the patency of blood vessels without resorting to invasive conventional x-ray angiography. The latter requires insertion of a catheter into an artery (usually in the groin) and carries a certain amount of risk (infection, vessel rupture, hematoma, occlusion, embolism, allergies to iodine dye, etc.). If one has an allergy to shellfish, this is a reason to avoid iodine dye. An MRA scan provides more detail than a basic MRI scan. It can help detect problems of the arteries and veins, such as a bulge in the wall of an artery (aneurysm), blockage of a blood vessel (by pressure from multiple cysts, fatty deposits or a blood clot), or a tear in the inner lining of a blood vessel (dissection).
CT Scan
A CT exposes one to radiation. The radiation dose is cumulative over a lifetime. The most common problem is an adverse reaction to intravenous contrast material. Intravenous contrast is usually an iodine-based liquid given in the vein, which makes many organs and structures, such as the kidneys and blood vessels much more visible on the CT scan. There may be resulting itching, a rash, hives, or a feeling of warmth throughout the body. These are usually self-limiting reactions and go away rather quickly. If needed, antihistamines can be given to help relieve the symptoms. A more serious reaction to intravenous contrast is called an anaphylactic reaction. When this occurs, the patient may experience severe hives and/or extreme difficulty in breathing. This reaction is quite rare, but is potentially life-threatening if not treated. Medications which may include corticosteroids, antihistamines, and epinephrine reverse this adverse reaction. Toxicity to the kidneys can result when a person is in kidney failure. This is an extremely rare complication of the intravenous contrast used in CT scans. Diabetics, dehydrated individuals, or patients who already have impaired kidney function are most prone to this reaction. Newer intravenous contrast agents have been developed, such as IsovueŽ, which have nearly eliminated this complication. Usually one must be fasting about 4 hours before having a CT scan done. If a woman were pregnant, then a better exam without radiation exposure would be an ultrasound. Though radiation from a CT is minimal; during the first three months of pregnancy, this exposure is too much for the unborn fetus.
MRI vs CT
If a choice can be made, MRI does not expose one to radiation. MRI might be more expensive but it is less harmful.
"The American College of Radiology also is leading campaigns called Image Wisely, to reduce unnecessary radiation exposure in adults, and Image Gently, to reduce exposure in children. The campaigns address growing concerns over the risk of cancers related to medical radiation, which has been estimated to cause up to 29,000 cancers a year. Researchers estimate that one-third of CT scans may be unnecessary, according to a 2009 report in the Archives in Internal Medicine."
Ultrasound
Ultrasound or sonography is a technique that uses sound waves to study and treat hard-to-view areas. It is a close up view of something within the body. Ultrasound is noninvasive, involves no radiation. The radiologist is able to view an organ very close with great detail such as within a water filled cyst vs. underlying normal tissue. An MRI is required for an expansive view of the organ in its entirety to determine organ size and the number of cysts.
In scanning with ultrasound, high-frequency sound waves are transmitted to the area of interest and the returning echoes. First developed in World War II to locate submerged objects, the technique is now widely used in virtually every branch of medicine. In obstetrics it is used to study the age, sex, and level of development of the fetus and to determine the presence of birth defects or other potential problems. Ultrasound is used in cardiology to detect heart damage and in ophthalmology to detect retinal problems. It is also used to thermally heat joints, relieving arthritic joint pain, and for such procedures as lithotripsy, in which shock waves break up kidney stones, eliminating the need for surgery. An ultrasound is useful for determining if the blood vessels of the legs are open and free flowing; also for determining the extent, which the carotid arteries are blocked or open.
Venogram
A venogram uses X rays to view blood vessels. This is an invasive procedure usually reserved for those times when other imaging studies are not sensitive enough to show a blockage, an aneurysm, a duct or some other anatomy. Physicians use this test to determine the extent of narrow, blocked, enlarged, or malformed vessels including the brain, heart, abdomen, and legs. When the arteries are studied, the test is called an arteriogram. If the veins are studied, it is called a venogram.
Scintigraphy for Within Cyst Infections
PET scan is used for detecting intracyst infections (infections within a cyst); and is especially useful for detecting tumors or solid tumor masses. PET scan is a form of
scintigraphy that uses gamma rays.
Medical scientists replace one of the oxygen molecules on glucose with fluorine (a slightly radioactive substance). When injected, this
radioactive substance goes straight to solid tumor masses.
This substance is called 18Fluoro2deoxyglucose (FDG).
Intracyst infections oftentimes are very difficult to diagnose because culture and sensitivity tests come back normal. Bacteria captured within a
cyst rarely crosses the cyst wall barrier. The bacteria
does not appear in great enough numbers in the blood or urine. Tagged white blood cell scintigraphy is one study available to determine if there is an infection within a cyst.
Leukocyte scintigraphy seems to be a very good study to help doctors solve a diagnosing dilemma.
Blood is withdrawn. Then the person's blood cells are spun down; the white blood cells are tagged and
re-injected back into the individual. Looking at the tagged white blood cells with imaging, doctors can see the leukocytes going straight toward the area of infection
like a magnet.
CT Virtual Colonoscopy
Virtual Colonoscopy uses ultra fast spiral multi-slice CT to look at the colon; these are sent to the radiologist who looks at it and makes a diagnosis. In children this requires no prep, so the diagnosis of Crohn's Disease is more readily seen. With CT, a three-dimensional picture of part of the body is put together from a number of images. In Europe and a few centers in the United States, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is being used for virtual colonoscopy. MRI uses radio waves to produce images. A potential advantage of MR imaging is that it doesn't expose the patient to radiation, as CT does. The procedure was first performed in 1994. Frail, elderly patients are more easily examined by Virtual Colonoscopy.
Scope Colonoscopy
The prep for standard colonoscopy for PKD'rs is GoLYTLEY or polyethylene glycol (PEG). More on colon preps and clear liquid diets. Avoid fleets phosphate soda with kidney disease. Review the pros and cons of virtual colonoscopy vs standard colonoscopy. A recent research published in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology showed purgatives containing sodium phosphate are an under-recognized cause of chronic kidney failure in the United States. Common bowel-cleansing drugs that include sodium phosphate are VisicolŽ, a prescription oral tablet, and the non-prescription product Fleet Phosphor-Soda. Researchers cite several potential factors that may contribute to the development of kidney problems from sodium phosphate solutions, including inadequate hydration, a history of high blood pressure and the use of non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Researchers from the Columbia College of Physicians and Surgeons in New York reviewed 7,349 kidney biopsies in their facility between January 2000 and December 2004 and found 31 patients who had kidney damage that was consistent with phosphate toxicity. Two-thirds of them had taken oral phosphate solutions prior to having colonoscopies.
Pill Camera for Colonoscopy
"FDA regulators green light a new smartpill that has been cleared as an alternative to receiving a traditional colonoscopy for some patients. Called the PillCam Colon 2, the smart pill houses two high-speed cameras, an LED that provides needed lighting, and a transmitter. Once swallowed, the smartpill captures a video recording of the GI tract as it moves through the system, and transmits the information to a hip-worn receiver for later review by a GI doctor. PillCam was approved as a direct de novo classification which is used for devices with low to moderate risk that have no equivalent on the market."
Mayo Pill for DNA Colon Cancer Screening
This pill called sDNA detects a common colon cancer gene. It does not require special prep or laxatives or a scope. No special preparation or restrictions are needed, it can be performed on mailed-in samples. This non-invasive stool DNA test was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration to use as a screening option for colorectal cancer. The test is called Cologuard and is available at Mayo Clinic. It was co-developed by Exact Sciences Corp. and Mayo Clinic.